In recent years, innovations in finance and accounting have revolutionized operations, and significant trends are reshaping the entire finance function. In all finance and accounting processes, whether bookkeeping, accounts payable, accounts receivable, or even complex analytics, a notable trend is the adoption of automation and AI. These innovative technologies have the unwavering potential to revolutionize finance and accounting.
There’s hardly any counterargument regarding the benefits of these technologies to streamline processes, reduce errors, and enhance decision making, and they also provide real-time insights into financial data. This departure from manual, time-consuming tasks has allowed finance professionals to focus on higher-value activities such as strategic planning and risk management.
In comparison to other methods, the use of innovative technologies in finance and accounting provides efficiency and precision in outcomes. For instance, machine learning algorithms can analyze large data sets and identify patterns, enhancing fraud detection and risk assessment at the same time. Moreover, blockchain technology has revolutionized how transactions are recorded, resulting in transparency and security in financial dealings. These advancements empower companies to make informed decisions while ensuring compliance with regulations. Conversely, conventional practices often involve data entry that’s prone to errors and time-consuming, leading to delays and potential discrepancies in financial reporting.
Innovative processes cover a range of activities including robotic process automation (RPA), predictive analytics, cloud-based accounting software, and digital auditing tools (see “Highly Impacted Activities”). RPA uses software robots to handle repetitive tasks such as data extraction and invoice processing, freeing up human resources for judgment-based strategic analysis. In the same way, predictive analytics leverages historical data, statistics, and algorithms to forecast future trends and patterns that can aid in processes such as budgeting and financial planning. Cloud-based accounting software enables real-time collaboration and data access, facilitating remote work and reducing the need for physical infrastructure, thus allowing the reduction of tasks and consolidation of work performed by several individuals on a team. Digital auditing tools enhance audit efficiency by automating testing procedures and improving accuracy in financial statements. These activities have advanced underlying processes such as journal entry, month-end close, accounts payable, purchase orders, invoicing, and vendor payments.
Highly Impacted Activities
|
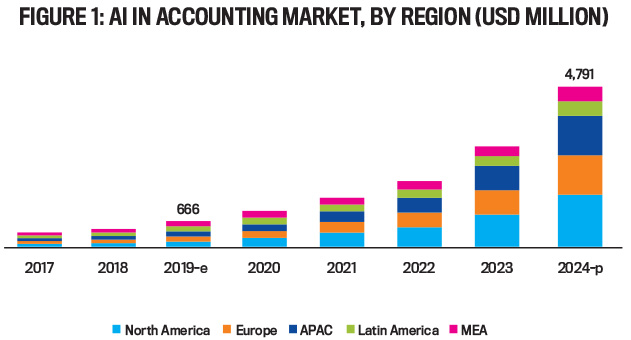
The adoption of innovative processes is impacting the way finance and accounting now operate, and it’s reshaping organizational, cultural, and work dynamics. Finance teams are transitioning from reactive postmortems to proactive analysis by leveraging data-driven insights that drive strategic decision making. With the advent of new technologies, the emphasis on continuous learning and upskilling has also become paramount. According to MarketsandMarkets, the market size of AI in accounting was $666 million in 2019 and is expected to grow to $4.7 billion by 2024 (see Figure 1). The shift toward remote work and digital collaboration has necessitated a more agile and adaptable work culture. Overall, these processes are improving the efficiency of accounting and finance functions, transforming how businesses approach financial management and cultivating a culture of innovation and adaptability.
Source: MarketsandMarkets, Artificial Intelligence in Accounting Market by Component, Deployment Mode, Technology, Enterprise Size, Application (Automated Bookkeeping, Fraud and Risk Management, and Invoice Classification and Approvals), and Region – Global Forecast to 2024.
Innovation in the Record-to-Report Process
Innovation in the record-to-report (R2R) process enhances operational efficiency. With routine and manual tasks being automated, finance teams can allocate more time to strategic analysis, data interpretation, and decision support. This transformation fosters a culture of continuous improvement and empowers finance professionals to provide valuable insights that drive business growth. This also helps organizations reap the benefits of streamlined operations, reduced costs, improved data accuracy, and a more agile approach to financial management.
Innovation in this area encompasses activities such as journal entry, reconciliation, and month-end close. It has become a driving force behind increased efficiency, accuracy, and agility in accounting and finance functions. Traditional manual handling of these tasks has often been time-consuming, error-prone, and resource-intensive. Technological advancements, particularly automation and data analytics, have revolutionized how these processes are executed, leading to significant improvements in the day-to-day management of financials.
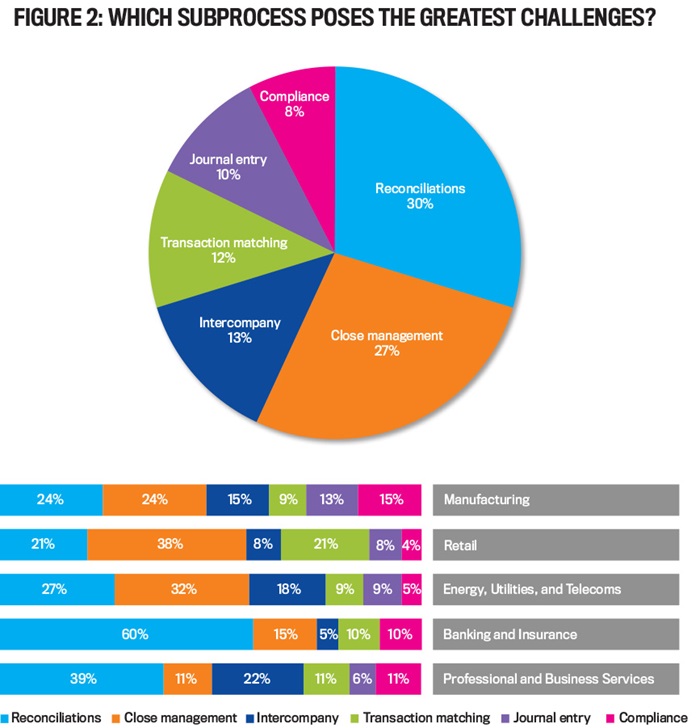
According to a survey by Trintech, the reconciliation process is the most formidable hurdle in the month-end process, making it the natural choice for initial automation efforts. The survey reveals that 27% of respondents consider the management of the closing process as their biggest challenge during month-end activities (see Figure 2). Further, 60% of those respondents from the banking and insurance sector identified reconciliation as their most significant hurdle during the financial close process. In most other industries, the issue of transaction matching remains relatively consistent, with 9% to 11% of respondents encountering this challenge. In the retail sector, however, this percentage doubles, highlighting the unique complexities faced by retailers in transaction matching.
Source: Trintech, Global Record to Report Benchmark Report, 2020.
Journal entry process. As technology advances, there’s a potential opportunity to increasingly build software solutions that allow for the automatic generation, approval, and posting of journal entries. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and ensures consistent application of accounting rules and standards.
AI-powered algorithms can analyze historical data and patterns to suggest appropriate journal entries, streamlining the process and reducing the risk of errors. Furthermore, automation can expedite the approval workflow and get input for journal entries from stakeholders, thereby enhancing collaboration among finance teams and providing real-time visibility into the status of entries. AI is capable of reading from requests that need a journal entry, analyzing transaction nature, identifying accounting heads, preparing entries, and posting them per the defined approval process.
Traditionally, journal entries involved manual data entry and validation, which were time-consuming and prone to errors. With advanced technologies like RPA and AI, journal entry processes have become more efficient and accurate. For example, AI has inbuilt logic that can automatically categorize and validate financial transactions based on historical data patterns. RPA bots are capable of executing these entries that not only reduce the risk of human error but also accelerate the process. This automation saves time and ensures that financial records are consistently accurate.
Balance sheet account reconciliation. The reconciliation process involves comparing two sets of records to ensure they match. This process has benefited immensely from technological innovation. Previously, reconciliations were often done manually, which required significant effort and time. Today, automated reconciliation tools leverage AI and machine learning to match and compare large volumes of transactions, accounts, and balances across multiple systems and to quickly identify discrepancies, exceptions, or anomalies, thus enabling finance professionals to focus on resolving complex issues rather than manually reconciling routine items. By reducing manual effort, organizations can achieve faster reconciliation cycles, improve data accuracy, and enhance overall financial transparency. These tools can import data automatically from banks and perform reconciliations. They can easily handle complex reconciliations, such as bank statement reconciliations and intercompany transactions. Unusual patterns identified in data by AI can be helpful for fraud detection and risk management as well.
Month-end close. The month-end close has the potential for significant transformation through innovative processes due to advancements in cloud-based accounting platforms and enterprise-wide integrated software applications that enable real-time collaboration and data sharing among cross-functional teams. This eliminates the need for physical proximity, increases productivity, and allows for simultaneous processing, review, and approval of month-end activities, ultimately shortening the amount of time to close. Automation of routine tasks, such as accrual calculations and variance analysis, helps expedite the month-end close and improves its accuracy. AI-driven predictive analytics can also anticipate potential bottlenecks or issues in the close process, allowing finance leaders to proactively allocate resources and address challenges before they impact the timeline. This automation also allows all the scheduled activities to be monitored, provides insights into the progress of the close, and analyzes the issues that might delay the close, allowing teams to proactively address these challenges.
Innovation in the Accounts Payable Process
The field of accounts payable has undergone a significant transformation with the integration of innovative technologies, particularly in automated purchase orders, invoicing, and vendor payment processing. Traditional manual processes in accounts payable often involved paper-based documentation, manual data entry, and lengthy approval workflows. Automation, AI, and digital platforms have revolutionized how businesses manage their payables, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings; automated and streamlined the payable process; and enabled a more strategic approach to financial management. The future of accounts payable with innovative technologies supports efficiency gains, enhanced vendor relationships, and opportunities for more proactive, strategic roles for finance professionals.
Purchase orders. Automated purchase orders have streamlined the procurement process by digitizing and automating the creation, approval, and systematic tracking of these documents. This eliminates the need for manual paperwork and speeds up the procurement cycle. AI algorithms can analyze historical purchasing data and patterns to optimize inventory levels, anticipate demand, and suggest the most cost-effective suppliers. Additionally, automated purchase orders facilitate better communication with vendors, ensuring accurate order fulfillment and reducing the likelihood of errors or discrepancies.
Invoicing. Paper invoices were traditionally prone to errors, delays, and lost documents. With automated invoicing, businesses can electronically receive and process invoices, reducing manual data entry and improving accuracy. AI-powered optical character recognition (OCR) technology can extract relevant information from invoices, such as invoice numbers, amounts, and due dates.
For example, if an invoice doesn’t match due to price variation, AI will detect the price difference and automatically correct it. After the defined approvals on the price change, the invoice is routed out for payment. Lastly, automated workflows can route invoices for approval based on predefined rules. These innovations accelerate the approval process, ensure timely payments, and enhance vendor relationships, which may enable organizations to take advantage of early payment discounts.
Vendor payments. Automated payment platforms enable electronic fund transfers, eliminating the need for physical checks and manual signatures. This results in faster and more secure transactions, reducing the risk of fraud or payment errors. Payment automation can also integrate with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, providing real-time visibility into cash flow and financial obligations. Also, advancement in blockchain technology is being explored to enhance transparency and traceability of cross-border payments, which also ensures compliance with regulations and lowers transaction costs.
Innovation in the Procure-to-Pay Process
Innovation in the procure-to-pay (P2P) process is reshaping how organizations manage every step, from approving vendors to paying invoices. The P2P process traditionally involved a lot of manual paperwork, communication issues, and a lengthy approval cycle. With the adoption of automation and AI, there’s more efficiency, visibility, and collaboration across the entire supply chain in the P2P process.
Vendor approvals. There are dramatic changes in the vendor approval process due to the implementation of advanced vendor management systems. These platforms use AI and data analytics to assess vendor performance, financial stability, and compliance history. This is a data-driven approach that helps organizations make informed decisions when onboarding new vendors. It reduces the risk of fraud and ensures alignment with business objectives. Additionally, automated workflows are used to route vendor approvals to the appropriate stakeholders, speeding up the approval process and providing a clear audit trail.
Purchase order management. With automated solutions, issuing purchase orders has become more streamlined and error resistant. Instead of manually generating and circulating paper-based purchase orders, organizations can leverage digital procurement platforms. These AI-powered systems can suggest optimal suppliers based on their history and negotiated terms, making purchasing decisions cost-effective. These automated purchase orders reduce data-entry errors and enable real-time tracking of orders, ultimately ensuring the timely delivery of goods and services.
Goods receipt process. The way goods are received has also been transformed. In the supply chain, advanced tracking systems and connected Internet of Things (IoT) devices allow organizations to monitor the movement of goods at any point in time. There are also possibilities for real-time visibility into shipments, ensuring accurate and timely delivery. AI algorithms can predict potential delays and simultaneously provide insights required for proactive management. Also, using automated alerts and notifications enhances communication, which enables quick resolution of any issues arising during the goods receipt process. Some technologies involve connected devices that have transformed goods receipt processes, including radio frequency identification (RFID) for automated wireless technology, gate cameras that record goods receipts automatically, and barcode scanners that digitize labels, ensuring correct accounting records.
Challenges of AI and Innovative Technologies
There’s no doubt that AI and other innovative technologies have brought significant advancements to finance and accounting processes. Still, they also present many challenges that organizations need to address, which depend on the selected technology and its implementation. The following are some important challenges associated with AI and other innovative technologies in finance and accounting.
Data quality and integration. Predictive analytics that uses AI algorithms analyzes historical financial data to identify patterns and trends, which allows organizations to make more accurate automation results, forecasts for budgeting, cash flow projections, and financial planning. These tools consider a wide range of variables and market factors that provide insights for informed strategic decision making. Yet AI and automation heavily rely on high-quality data. An inaccurate or incomplete data set can lead to flawed insights and biased decisions. AI systems can consume biases present in historical data, leading to biased outcomes in decision making. This can be due to onetime transactions required for correct accounting applicable to a specific time. Mitigating bias and ensuring ethical AI usage require ongoing monitoring and refinement of algorithms. Also, integrating data from disparate sources can be complex and time-consuming tasks that require careful data governance.
Adoption and change management. Automation in finance processes involves AI systems that can understand, interpret, and process unstructured data from various sources, such as invoices, contracts, and emails. This technology can automatically extract relevant information, classify documents, initiate workflows, reduce manual data entry, and improve accuracy. Implementing these new technologies, however, often requires changes to established processes and workflows, and employees may resist implementing them. This resistance to change will require extensive training for employees to fully realize the benefits.
Cybersecurity and data privacy. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of transaction data to detect irregular patterns and anomalies indicative of fraudulent activities. Machine learning models continuously learn from new data and improve their ability to identify emerging fraud trends or prevent potential financial losses. As more data is processed and stored digitally, however, there’s an increasing risk of data breaches and cyberattacks. Organizations need to implement a strategy for the robust protection of sensitive financial information and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
High upfront cost. While innovative technologies can lead to cost savings in the long run, the initial investment in acquiring and implementing these technologies can be significant. Organizations that focus more on the return on investment and payback will need to allocate resources effectively and carefully.
Complexity and technical expertise. Technology such as natural language processing (NLP) enables computers to understand and process human language, which is particularly useful for tasks like contract analysis and due diligence. NLP-powered tools have the ability to review contracts, extract key terms, and assess compliance with legal, regulatory, and financial standards. Integrating AI and other innovative technologies requires specialized technical expertise, however. Finding and retaining such skilled professionals can be a challenging task.
Incorrect outcomes. These innovative AI models have the ability to analyze complex risk scenarios by considering multiple variables and historical data that help finance teams assess and mitigate risks more effectively. But, as mentioned previously, AI systems can present biases in historical data that lead to incorrect outcomes. AI systems perpetuate biases present in historical data, and biases can emerge from the data itself or be introduced by underlying algorithms that can lead to unfair decisions. Finance and accounting professionals must take steps to audit AI systems for biases and errors regularly. This requires them to use diverse and representative data for training, promote transparency, and adhere to ethical frameworks. By addressing these concerns, finance and accounting professionals can harness the benefits of AI while ensuring ethical standards and fairness in their financial processes and data analytics. Therefore, ensuring ethical AI usage and minimizing bias is a critical challenge that needs to be addressed.
Developing the Next Generation of Finance and Accounting Professionals
Due to the faster adoption of innovative processes such as automation, forward-thinking finance and accounting professionals are proactively preparing to minimize the negative impact on their career. Finance teams are recognizing the importance of acquiring new skills and taking steps to adapt to emerging trends. The following are some skills that will help to make the best use of AI and other innovations in accounting and finance.
Acquiring data analytics skills. Gaining data analytics skills is becoming a cornerstone for finance and accounting professionals, enabling them to analyze and interpret large data sets to extract meaningful insights that help inform decisions. In addition, acquiring proficiency in data visualization tools and techniques enhances their ability to communicate faster insights. A recent LinkedIn poll of finance professionals showed that 86% of respondents agree that Excel-based visualizations are still preferred due to their flexibility and features. This preference for Microsoft Excel over specialized data visualization tools such as Power BI and Tableau is possibly due to its familiarity, accessibility, ease of use, and flexibility for ad hoc reporting. The interface of Excel is user-friendly, and extensive customization options make it a go-to choice for creating quick reports and conducting fast analyses. It can also be accessed offline, which most likely contributes to its popularity. Organizations often adopt a hybrid approach to harness long-term benefits in complex data analytics and visualization, combining Excel for ad hoc tasks with specialized tools such as Power BI and Tableau for comprehensive data management, automation, and visualization. This will achieve a balance between flexibility and advanced capabilities.
Learning structured query language (SQL) and coding. Finance professionals are required to extract data from a database to perform analysis. This requires an understanding of SQL and primary coding languages such as Python and R. These skills are available because they allow finance professionals to manipulate data, automate processes, and develop custom solutions for their required analytical needs.
Embracing AI and machine learning. Future finance professionals are taking courses to familiarize themselves with AI and machine learning concepts. They don’t need to become experts in developing AI algorithms, but they do need to understand how AI works. It can also position them to collaborate effectively with data scientists and IT teams.
Adopting automation tools. The finance team is learning to use RPA tools to streamline repetitive tasks, reduce errors, and increase efficiency. Some familiarity with automation platforms helps them to deal with automated processes and also to identify processes that can be automated and implemented with RPA solutions.
Enhancing communication and collaboration. These technologies facilitate real-time collaboration, and professionals are honing their communication and teamwork skills. This will help them work seamlessly across departments and collaborate with cross-functional teams.
Staying current with regulatory changes. Professionals must continuously update their knowledge of industry regulations and compliance requirements. They must understand innovation-related legal and ethical standards to ensure accurate financial reporting and risk management.
Developing a leadership and innovation mindset. To prepare for the future, finance and accounting professionals are developing leadership skills and an innovation mindset. This will allow them to embrace change and seek opportunities to drive innovation within their organizations and position themselves as forward-thinking strategists.
Activities Not Impacted by AI
There are certain areas in finance and accounting that are less impacted by AI due to the nature of the tasks involved. These areas include strategic decision making, relationship management, complex financial analysis, regulatory compliance, and innovative problem solving (see “Least-Impacted Activities”). While AI can provide valuable data-driven insights, strategic decision making relies on human judgment because of contextual understanding and the ability to evaluate nonquantitative considerations. Relationship management is also critical for client and stakeholder interactions that hinge on interpersonal skills and human empathy that AI can’t replicate. Similarly, complex financial analysis demands in-depth expertise and interpretation, and, even with AI assistance, the human touch remains indispensable. Also, regulatory compliance requires the correct interpretation of complex regulations, which goes beyond AI’s capabilities right now. Finally, innovative problem solving often involves creative thinking, considering unconventional solutions, and adapting to dynamic situations.
Least-Impacted Activities
|
In this fast-moving, dynamic environment, future finance and accounting professionals are actively preparing for the impact of innovative processes by acquiring diverse skills, from data analytics and coding to leadership strategies and an innovation mindset. Finance and accounting professionals must position themselves to make the best use of AI and other innovations in accounting and finance. Therefore, by combining technical expertise, a strategic mindset, and strong interpersonal skills, they’ll be poised to excel in this landscape.
AI and other innovative technologies have the unwavering potential to revolutionize finance and accounting. They automate routine tasks, enhance analysis, and improve decision making. Yet some challenges and impacts aren’t uniform across all aspects of the field. This will require agility to present themselves as flexible enough to surmount these challenges. The successful integration of AI requires a comprehensive approach, a broader understanding that addresses several considerations around technical tasks, ethical standards, and organizational culture, and simultaneously capitalizing on the strengths of technology and human expertise.
Further ReadingCameron Putty, Automating Data Entry with AI, Thoughtful, August 22, 2023.
Trintech, Global Record to Report Benchmark Report, 2020.
Gary Waylett, Is It Possible to Achieve Fully Automated Bank Reconciliations? BlackLine Magazine, January 17, 2021.
Marco Porru, Implement SAP S/4HANA Quality Control of Goods Receipt with SAP Internet of Things, Smart Sensing, SAP, October 18, 2021.
Transformative technologies (AI) challenges and principles of regulation, Digital Regulation Platform, August 9, 2023.
Neil Perry, Top 10: Generative AI platforms in procurement, Procurement, August 1, 2023.
|

October 2023